
There are few things that matter more to asset management than the maintenance schedule. An effectively planned schedule is often the difference between unplanned downtime and maximum productivity.
Here, we’ll guide you through scheduled maintenance and everything you need to know to keep your critical equipment up and running when your facility needs it most.
What is scheduled maintenance?
Generally speaking, all maintenance tasks are designed to serve one common purpose: To prevent, mitigate or eliminate the ramifications associated with asset failure.

Why? Because downtime – whether planned or not – is a major detriment to business continuity. Think about it: When critical equipment goes down for repair, its corresponding function is thrown for a loop and productivity declines. According to IBM, the average cost of planned downtime for an enterprise is $5.6 million in a single year. As if that’s not bad enough, unplanned downtime costs businesses 35% more per minute.
That’s why maintenance work is so concerned with maximizing equipment availability – and scheduled maintenance is no different. Simply put, scheduled maintenance refers to any service work performed on a set timeframe, repeating interval or in immediate response to a work order.
For example, you might perform a scheduled maintenance task on a specific asset once a year. Or, your maintenance schedule might book routine maintenance or safety checks every 30, 60 or 90 days for more critical equipment.
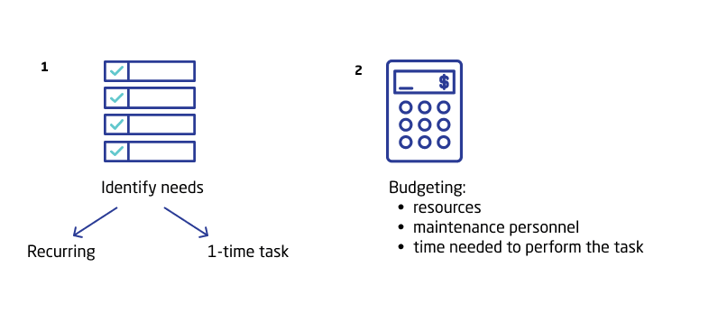
Typically, the scheduled maintenance workflow begins with identifying your need and determining if it requires a recurring or one-time task. Once decided, a maintenance planner would budget the necessary resources, maintenance personnel and timing needed to perform the task in either instance.
Scheduled maintenance vs. planned maintenance
When it comes to understanding scheduled maintenance, you also need to know how it relates to planned maintenance. Although the two terms are often used interchangeably, they differ in a few noteworthy ways.
To avoid confusion, let’s break them down individually:
Planned maintenance:
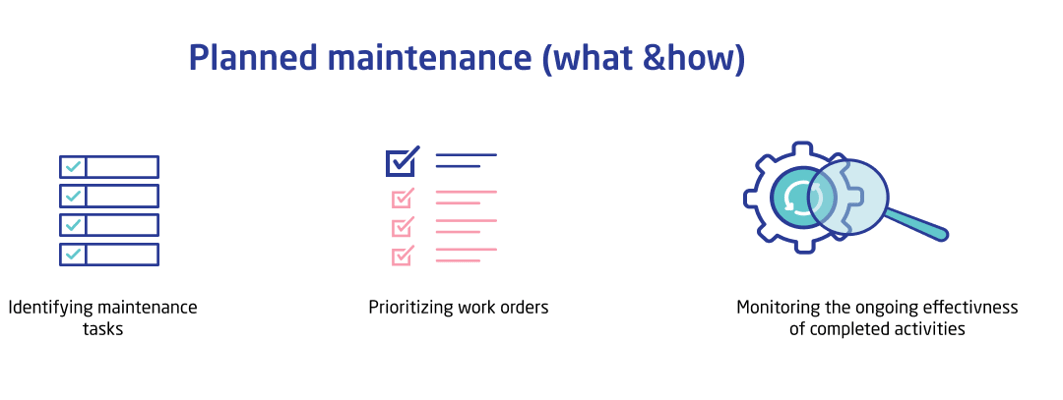
Planned maintenance is an anticipatory process of determining future equipment and maintenance needs. In other words, it involves identifying maintenance tasks, prioritizing work orders and monitoring the ongoing effectiveness of completed activities.
Central to this process is detailing the materials, parts and tools required to carry out the work order most effectively. Notably, planned maintenance takes on many strategies, including reactive maintenance, predictive maintenance and preventive maintenance. No matter which approach any given task takes on, the planning process accounts for the necessary resources to get the job done right.
Scheduled maintenance:
In contrast, scheduled maintenance is more concerned with detailing which technician will be completing the work order and when.
Generally, a scheduled maintenance service occurs after an issue has already been identified, such as when you notice a motor is no longer functioning. However, you can also take a proactive approach by completing tasks on a set scheduled maintenance interval.
The bottom line: Planned maintenance is all about what and how maintenance activities will be performed, whereas scheduled maintenance is about when they’ll be performed and by whom. Ultimately, these matters are two sides of the same coin, and neither can work without the other. Planned maintenance depends on effective scheduling, just as scheduled maintenance relies on smart planning.
What to consider when you’re planning scheduled maintenance
It’s worth noting that while maintenance of any type is a necessary disruption, it’s still a disruption to operations. Even though scheduled maintenance tasks are critical to ensuring the uptime and reliability of your business’ most important equipment, they can still curtail your workflows, if only temporarily.
That’s why it’s imperative to plan your routine maintenance activities as optimally as possible. Here’s what you’ll need to keep in mind when planning your maintenance schedule:
Availability of labor
This is where you’ll account for the technicians responsible for completing your scheduled maintenance service. You have to consider the availability of your maintenance team, as well as their skill sets. The most efficient way to ensure quality of work is to assign your technicians to tasks that suit their abilities.
Operating hours
If at all possible, schedule your safety checks, performance checks and other maintenance activities outside of regular business hours. This will ensure that productivity isn’t derailed by maintenance operations during the work day.
Priority of maintenance task
Of course, certain maintenance tasks are mission-critical the moment that an issue is identified. When equipment goes down for emergency repairs, those activities can’t wait. Even more importantly, when conditions pose a threat to health and safety they need to be mitigated as quickly as possible.
Scheduling other tasks, however, is a bit more complicated. Calculating your scheduled maintenance critical percent (SMCP) can help you prioritize maintenance in relation to their frequency of occurrence. The higher the percentage, the greater the priority. This allows you to optimize maintenance activities in a way that decreases unplanned downtime without causing a disruption to critical workflows.
Calculating SMCP
 There may be times when scheduling becomes backlogged and routine maintenance activities are delayed. SMCP helps you dig through this backlog and get ahead of your looming pile of tasks.
There may be times when scheduling becomes backlogged and routine maintenance activities are delayed. SMCP helps you dig through this backlog and get ahead of your looming pile of tasks.
To calculate SMCP, you need to know how many days late your maintenance task is and how many days are between each task in an ideal scheduled maintenance interval. Here’s the formula:
- SMCP = ((days late + days in cycle) / days in cycle) x 100
This metric is good for comparing tasks and prioritizing one over another, but be sure to keep in mind the other critical factors when planning scheduled maintenance.
How to maximize the benefits of scheduled maintenance
Scheduling maintenance activities in an organized, prioritized, and efficient manner is one of the tentpoles of effective asset management. Through scheduled maintenance, your facility stands to gain a variety of benefits.
Benefits of scheduled maintenance
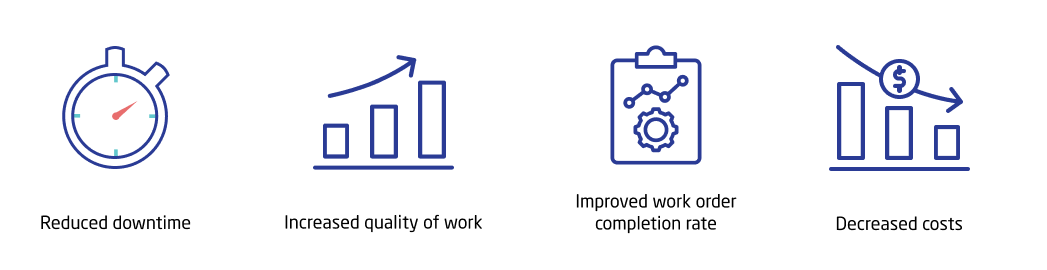
- Reduced downtime: Strategically scheduling and planning maintenance activities allows you to avoid interruptions to your day-to-day operations while improving asset reliability. Whether it be scheduling work outside of operating hours or during opportune times of the work day, this is the best way to ensure maximum productivity.
- Increased quality of work: Assigning the most optimal technicians to any given task not only means the job will be completed effectively but also that asset life expectancy will increase. Plus, you’re empowering your maintenance team to succeed by making the best use of their abilities.
- Improved work order completion rate: According to Plant Engineering, the average facility spends 19 hours each week on scheduled maintenance. Optimizing your maintenance schedule means enabling your technicians to perform their best. In turn, your work orders can be completed on time and at an accelerated pace.
- Decreased costs: Downtime and equipment failure are extremely costly to your business. Longer asset lifespans and fewer failures equate to more productivity, higher revenues and fewer missed opportunities.
However, optimizing your maintenance schedule is easier said than done. With the force multiplier of a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS), you can take your scheduled maintenance to the next level. CMMS monitors equipment usage, leverages maintenance histories, and prompts work orders at the most optimal moment. It helps maintenance planners view their available resources and schedule tasks at the most effective and least disruptive opportunities.
