In the new release for October 2019, Microsoft has announced a lot of new capabilities and features of Dynamics 365 and one of them is Asset Management.
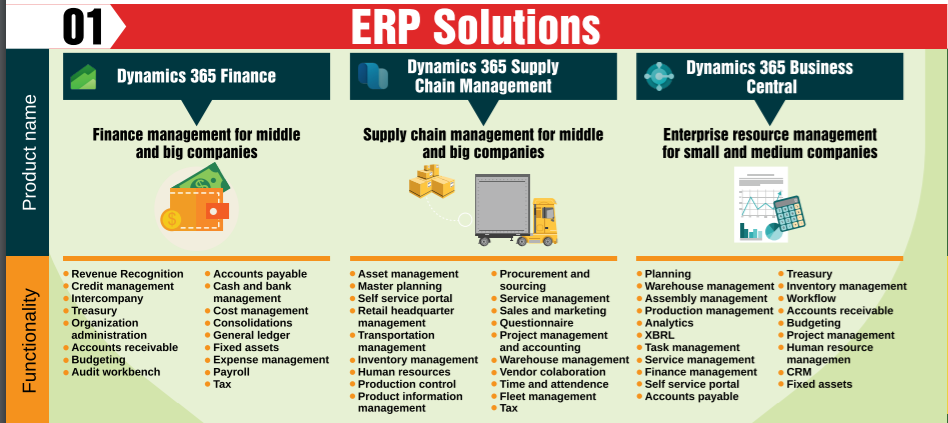
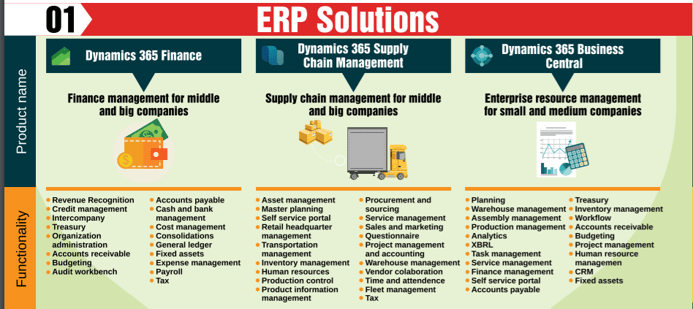
- Microsoft ERP solutions are: D365 Finance and D365 Supply Chain Management and D365 Business Central.
- With Asset Management module you improve asset lifecycle maintenance, planning and estimation of maintenance and use different maintenance strategies within one solution.
- There are 5 maintenance models: reactive maintenance, scheduled maintenance, condition based maintenance, predictive maintenance and cognitive maintenance.
As of now, Microsoft ERP solutions has been divided into 3 sections: D365 Finance and D365 Supply Chain Management and D365 Business Central.
NOTE: Asset Management is an additional module for Supply Chain Management
Microsoft Asset Management: What you need to know
Asset Management is an advanced module in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management for managing assets (objects) and maintenance work orders.
Asset Management Module Benefits:
Better maintain your assets lifecycle by tracking and monitoring the most important KPIs to improve the overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) of your critical assets.
More effectively plan and predict maintenance to maximise the durability and performance of significant assets while reducing costs and production downtime.
Convenient different maintenance strategies management—predictive, corrective, condition, and preventative—with a single solution.
Microsoft Asset Management Features
The image below is an illustration of the interfaces to other modules in Finance and Operations.
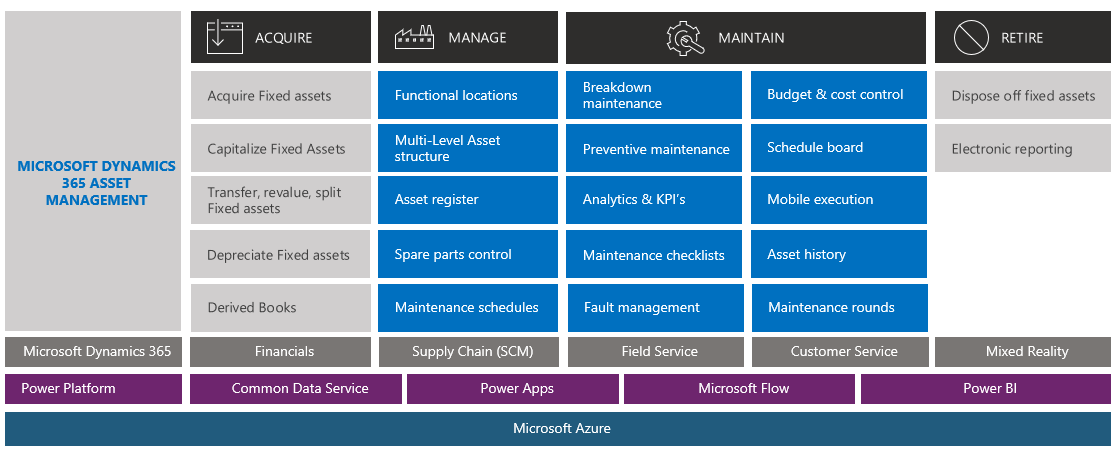
5 x Maintenance Models:
Value returned to the Enterprise
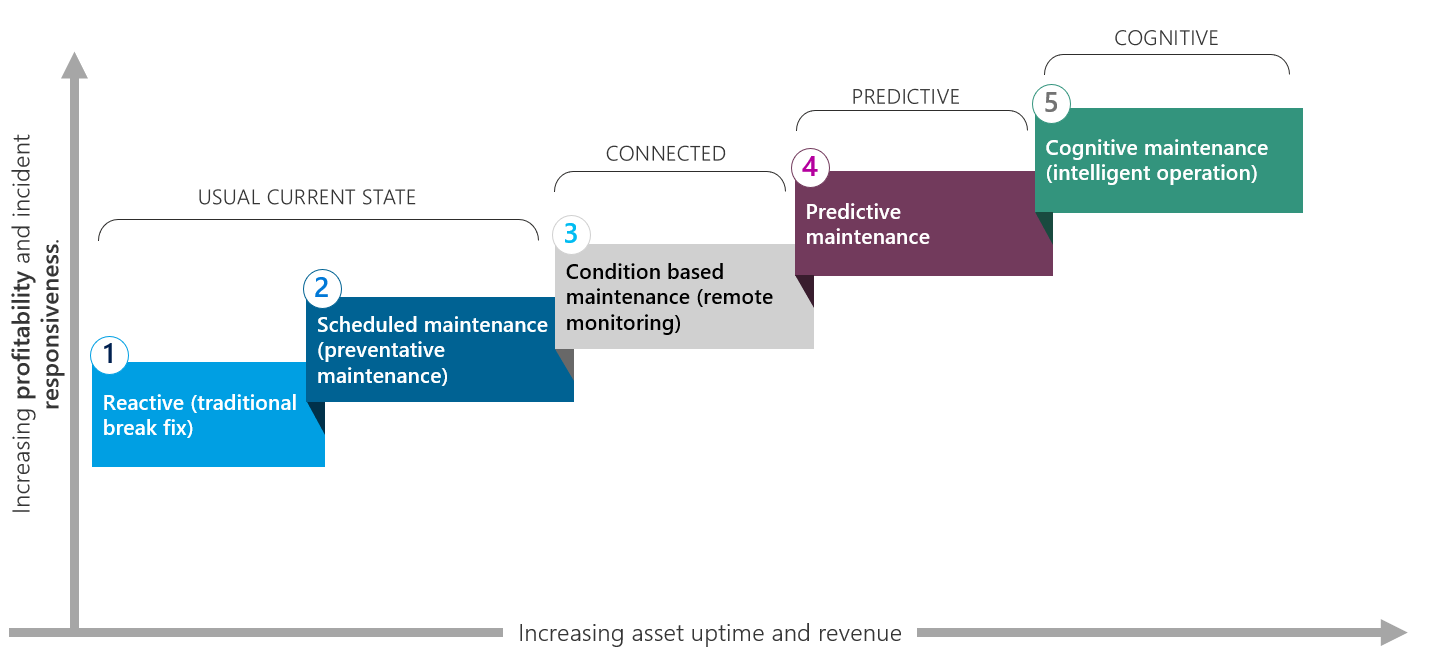
1. Reactive (traditional break fix)
Repair prompted by customer request.
2. Scheduled maintenance (preventative maintenance)
Repairs and services based on a fixed schedule regardless of condition or meet regulation.
3. Condition-based maintenance (remote monitoring)
Condition is monitored continuously using operating parameters to assess health
and indicate maintenance needs via real-time alerts.
4. Predictive maintenance
Remaining Useful Life (RUL) for critical components determines asset health and pairs efficient operating range measures, usage patterns and repair history to improve maintenance planning.
5. Cognitive maintenance (intelligent operation)
Autonomous actions are taken to ensure maximum asset utilization and efficiency. Maintenance is automatically scheduled in consideration of operating health and maintenance logistics including parts, consumables, tools and resource availability.